By Aravli Paliwal
~ 9 minutes
Earlier this summer, I was graciously given the opportunity to shadow a private-practice oncologist/hematologist in the Dallas area. There, I gained a clear understanding of what a career in STEM entails, learned how doctors approach complex cancer cases, and secured an inside view into the emotionally taxing yet deeply rewarding work of an oncologist.
What does an Oncologist’s career look like?
At the ground level, an oncologist’s job involves diagnosing and treating cancer. They play a central role in administering cancer treatments and developing long-term plans. There are three main types of oncologists:
- Medical Oncologist: Dr. Nair, whom I shadowed, practices as a medical oncologist. These doctors use targeted therapies like chemotherapy and immunotherapy to treat cancers.
- Surgical Oncologist: Surgical oncologists perform biopsies and remove tumors through surgical procedures. Usually, after a medical oncologist has successfully shrunk a tumor through targeted therapy, a surgical oncologist will excavate the remaining piece.
- Radiation Oncologist: As the name suggests, these doctors treat cancer through radiation therapy.
Dr. Nair works as a hematologist-oncologist. Because cancer often involves blood and bone marrow (leukemia, lymphoma, myeloma), having training in both oncology (solid tumors) and hematology (blood disorders) allows a doctor to treat a wider variety of patients without having to refer them to another clinic. Also, in the U.S., most oncologists need no extra schooling to end up board-certified in both.
Typically, becoming an oncologist requires about 14-16 years of school. This includes a four-year undergraduate program, where students generally major in biology, chemistry, mathematics, or physics. Then, students take the MCAT, or the Medical College Admission Test, and attend medical school to earn their MD. After four years of medical school, doctors attend a three-year residency program. Finally, they complete a three-year fellowship program, subspecializing in oncology or hematology-oncology. Oncologists typically finish schooling in their mid-thirties, and though they spend most of their twenties in schooling, many agree that this time is fully necessary due to the extensive information students have to understand.
A central part of an oncologist’s job is responding to a wide spectrum of questions, ranging from emotional ones like “if the tumor is getting bigger, do I have less time to live?” to straightforward questions like, “if I eat and sleep more, will I have more energy the next morning?” Sure, many of these questions become routine over time, but it’s that rare, complex one that truly tests a doctor’s knowledge and, when answered well, builds even more trust between the patient and their provider. Because cancer is such a serious topic, patients seek oncologists who make them comfortable, and the best way to provide that security is by easing their uncertainties and reinforcing confidence in their provider. This is exactly why those 14 long years of medical training matter so much.
The Difference Between Private Practice and Clinic
Dr. Nair is affiliated with the broader group Texas Oncology and practices at Medical City Dallas, but before going in to shadow her, I had no idea what the difference between a private practice and a clinic was. Here is an easy way to break it down:
- Private practice: When a doctor or group of doctors owns, manages, and runs their own medical office. Like a business, they hire staff, manage billing, and run their own practice from top to bottom. Though private practice intersects the two contrasting fields of medicine and business, these doctors have more flexibility when not working for a large hospital or healthcare system.
- Clinic: Usually affiliated with a larger group, hospital, or university. Doctors who work as part of a clinic follow the protocol set up by a broader employer and focus less on business and management.
Highlight Patients
You may think that looking at cancer gets repetitive after a while, and maybe you’re right- but in the two weeks that I shadowed Dr. Nair, we saw a wide variety of patients that kept me quite interested. Often, it wasn’t the cancer or condition that made them memorable, but their personality, and the reminder that cancer does not discriminate. People from all walks of life, rich or poor, tall or short, male or female, can be struck by the disease at random and affected in similar ways.
1. Female, mid-40s, obese
This patient was on blood-thinners that were administered by the hospital. Upon arriving home, she purposefully took double the prescribed dose for a few days. With the alarmingly high dosage this patient was taking, her gums would bleed when brushing her teeth, and minor cuts would bleed profusely without stopping. Suddenly, the patient formed a massive internal hemorrhage in her stomach, and was rushed to the ICU where she took a break from blood thinners and recuperated.
2. Female, mid-30s
This patient was aware she had a tumor in her lungs, but didn’t know the extent of its spread or whether it was even malignant. As the cardiothoracic surgeon opened her chest to perform a biopsy and assess the situation, he found that the cancer presented as stage 4 and had spread extensively throughout the lungs. After removing substantial diseased lung tissue, the patient’s remaining lung capacity was too low to sustain oxygenation. Therefore, she was placed on a ventilator that essentially acted as a pair of bedside lungs, pumping air for her.
3. Female, early-60s, groaning in pain
As Dr. Nair and I walked into the patient’s room, she was lying on the bed, groaning and screaming in severe pain. This woman had a pancreatic tumor, one of the most painful types of cancer, due to the tumor pressing on bunches of nerves and organs in the abdomen and back. Though she was fully lucid, the pain was preventing her from formulating complete thoughts or ideas, and her husband described that she could not eat properly or move around without a wheelchair. Dr. Nair told the couple to visit the ER within the hospital immediately, so that the patient could be administered stronger pain medications.
The role of women in healthcare
One thing that really stuck out to me was the number of women who worked in the office with Dr.Nair. Out of the three oncologists, only one was a man, and the rest of the staff, including the P.A. and infusion nurses, were all women.
In fact, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics; around 77.6% of all healthcare workers are women. However, we hold a disproportionately small number of leadership positions compared to men. Where 77.6% of healthcare workers are women, only about 38% of all physicians are women.
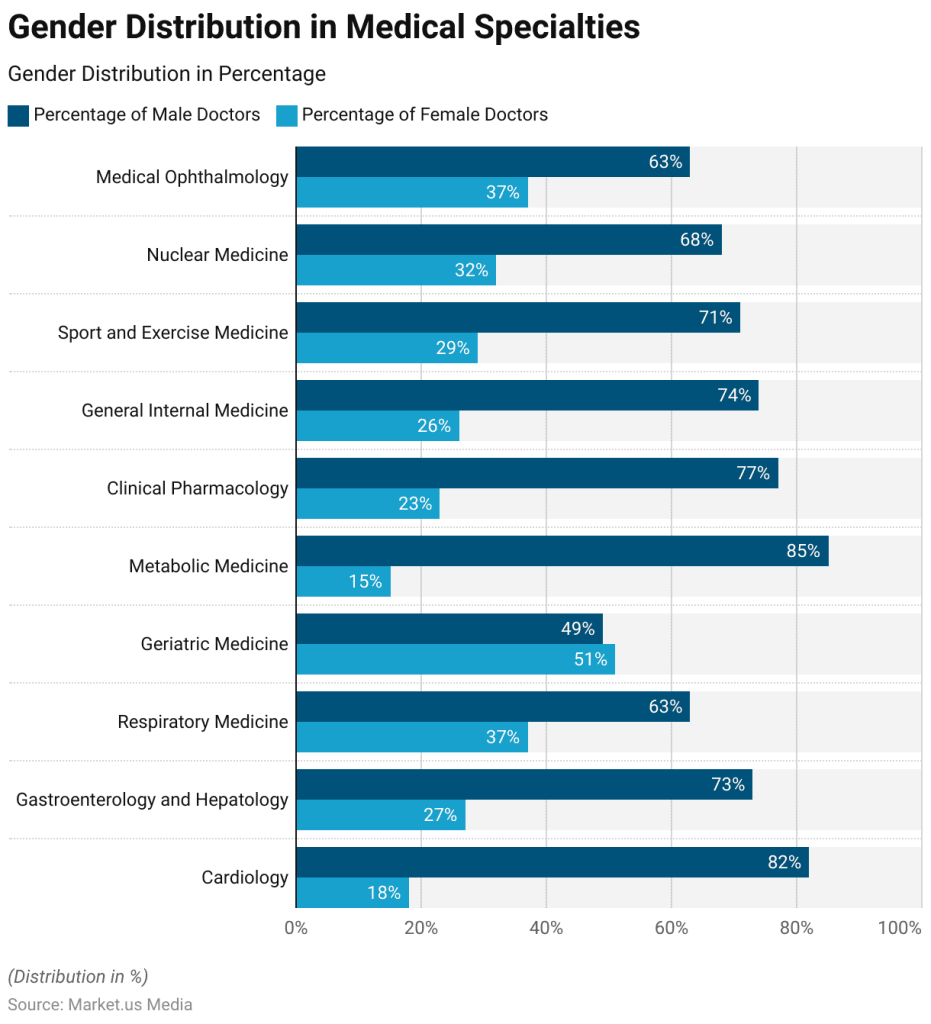
Despite the gender gap that still exists today, equality growth in the last 20 years alone has been monumental. According to the Association of American Medical Colleges,
“From 2004 to 2022, the number of women in the active physician workforce increased 97%.”
Going forward, the future looks bright too. In 2019, women for the first time accounted for a majority (50.5%) of students enrolled in medical school in the United States. Today, women account for about 54.6% of medical school students. As women make up the majority of medical school graduates, the number of physicians in the coming years will consequently increase.
Conclusion
Before I arrived at the oncologist’s office, I pictured a gloomy waiting room filled with silent, dejected patients. Instead, I discovered something completely different. People tend to imagine only the sickest patients at a cancer clinic, the ones who are dying. But they often forget about the many who are improving, on the uphill climb, and who see the doctor’s office not as a place of punishment or despair, but as a lifeline that offers hope and light at the end of the tunnel.
Seeing this side of cancer care reshaped my view of healthcare entirely. It made me realize that medicine isn’t just about treating disease and sending patients on their way, but instead creating an environment where people are given a reason to keep fighting.


Leave a comment