By Montserrat Tang
~ 9 minutes
The Hot Hell of Boilers
As someone born and raised in New York City (NYC), I can attest to the urgent need to upgrade the city’s climate control infrastructure. Current systems are outdated and hinder the city’s ability to meet emissions goals and address global warming; the encapsulation of this problem is the boiler. A staggering 72.9% of heating in NYC comes from fossil-fuel-burning steam boilers, one of the most carbon-intensive options available. Tenants of apartments pay for the maintenance of centralized boilers without control over the temperature, leading many to open their windows in winter to release excessive warmth. This heat and the fossil fuels used to produce it are wasted, highlighting the inefficiency and impracticality of NYC’s existing infrastructure.

Even when this heat remains indoors, steam boilers are only about 80-85% efficient at burning fossil fuels. Up to a fifth of a boiler’s fuel does not generate usable heat, but burning it still releases vast quantities of pollutants like CO2, exacerbating climate change. Furthermore, boilers continue to lose efficiency during their lifetimes and require frequent maintenance and replacement. While steam boiler systems were revolutionary in the 19th century, they may now become obsolete as NYC implements a technology that could change how the world thinks about climate control.
The Cool(ing) Mechanics of Heat Pumps
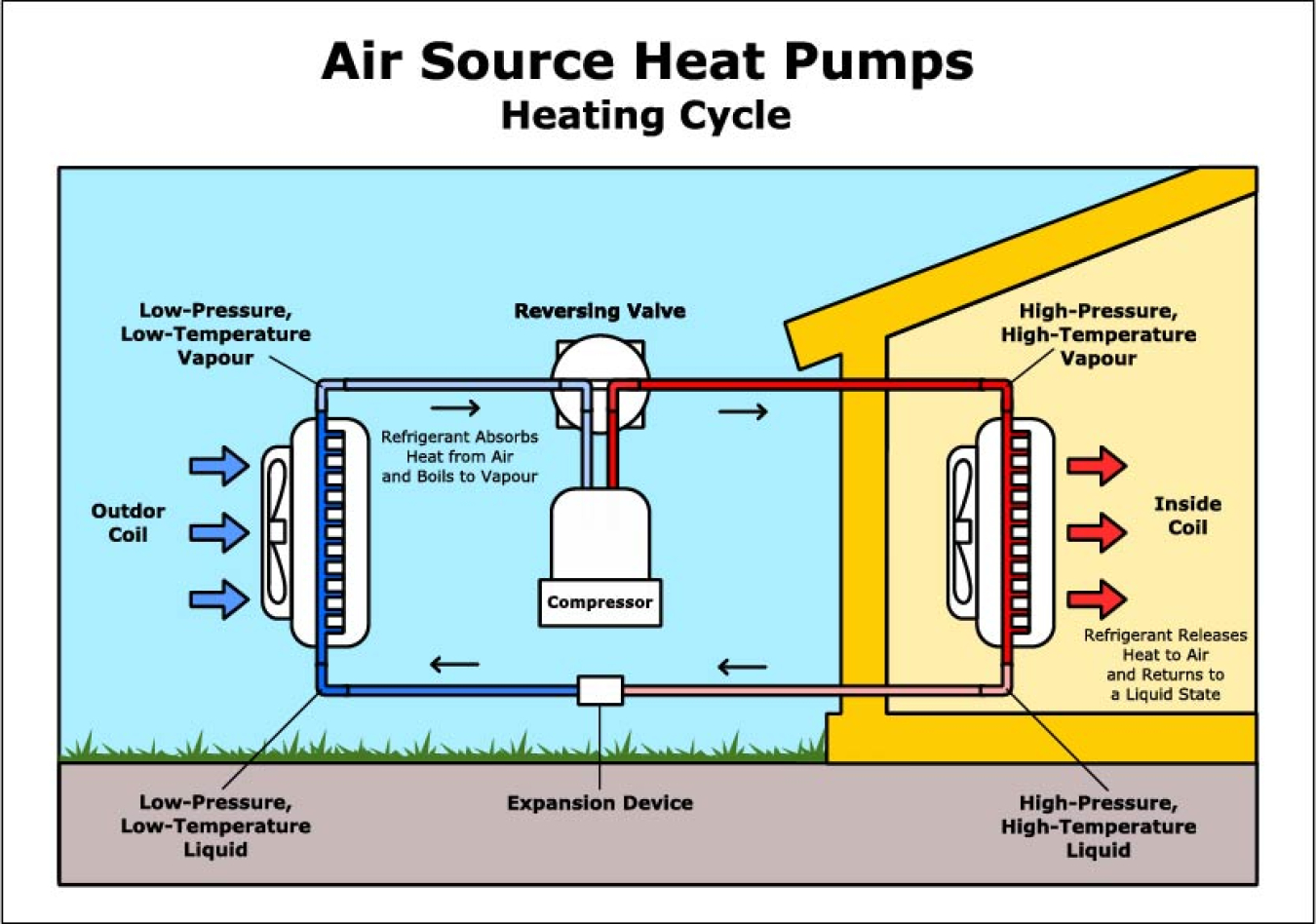
The innovation behind heat pumps comes from the mantra of use what is given; instead of generating heat through combustion, they simply move existing warmth between two places. Most of these fully-electric pumps remain functional well below 0℃, even though it may seem like there is no warmth to be moved. This operative capacity allows them to have heating efficiencies of 300-500%! Because of this, International Energy Agency partner Yannick Monschauer estimates that “Heat pumps could bring down global CO2 emissions by half a gigaton by the end of this decade.”
Heat pumps work by operating on the Second Law of Thermodynamics (SLOT), which states that heat will move from a hotter object to a colder one. In the wintertime, the pumps pull in outdoor air and blow it over fluids (called refrigerants) held in a closed-loop system. The air transfers warmth to the cold refrigerants through SLOT, and the heated fluids turn into gas. Heat pumps can work in freezing temperatures because these refrigerants have such unusually low boiling points, allowing them to vaporize easily; one of them, Refrigerant 12, has a boiling point of just -21.64°F!
The hot, gaseous refrigerants move into a compressor that compacts their molecules, making them even warmer. They then flow through a coil that exposes them to indoor air, and the refrigerants release their warmth inside through SLOT. As the refrigerants cool, they condense back into liquid and pass through an expansion valve, decreasing their temperature further. They move to an outdoor coil and are ready to restart the process, continuing to warm cold homes during the winter.
Even more significantly, heat pumps have reversing valves that switch the flow of their refrigerants. These valves allow the pumps to cool homes by pushing out warm, indoor air in the summertime. Thus, heat pumps make air conditioners, boilers, radiators, and related piping unnecessary, freeing space and alleviating material and labour costs that typically get passed on to homeowners.
Heat pumps in NYC
In 2024, NYC pledged to have heat pumps provide 65% of residential heating, air conditioning, and water-heating needs by 2030. This shift would drastically reduce the city’s carbon emissions from the climate control sector, which contributed to 10% of global energy-related CO2 emissions in 2021.
This pledge is logical both environmentally and practically: having one heat pump replace two systems saves valuable space, lowers costly installation and maintenance fees, and reduces energy demands. The NYC government realized this potential and signed a $70,000,000 contract to install 30,000 window heat pumps in NYCHA buildings, better known as public housing. Two heating companies, Midea and Gradient, will provide these units.
In late 2023, Gradient installed 36 preliminary test units in NYCHA buildings. Most NYC steam boilers, including those in NYCHA’s current system, are powered by gas with oil reserves in case of an emergency. Gradient found that their pump can lower tenants’ heating bills by 29-62% on moderate winter days compared to gas-powered boilers. Savings are as high as 59-78% compared to oil-burning boilers. In testimonials that Gradient collected, NYCHA tenants noted the heat pumps’ impressive air filtration, heating, and operational capabilities. Midea conducted similar tests and soon plans to release its heat pump for public purchase.
The Cold Drawbacks of Heat Pumps
Although technological faults remain, NYC is continuing its plans to install and promote heat pumps to replace its intensive, outdated systems. For one, Midea’s upcoming pump will cost ~$3,000 per unit, greatly exceeding the combined price of ~$460 for their bestselling, single-room heating and cooling systems. This is a misleading comparison, however, because heat pumps also act as heating systems. The technology can lower electricity and fuel bills over an extended period, but the current price point makes heat pumps an unaffordable investment for many households – despite government subsidies and incentives. Even the NYC government’s bulk order of Midea and Gradient pumps averages over $2,300 per unit.
Furthering the inaccessibility of these systems, the most advanced, aesthetically pleasing, and apartment-friendly heat pumps can only heat and cool individual rooms. This means that multiple units must be purchased, installed, and powered to service a home, and each must be replaced about every 20 years. Still, NYC’s firm stance on heat pumps indicates the climate control systems’ proven efficacy, practicality, and sustainability.
Heat Pumps Globally, and Plans for the Future
While technological challenges remain, NYC is continuing to deliver on its pledges. This decision on heat pumps is being made throughout the United States (US). In 2022, heat pump sales in the US significantly outpaced those of gas furnaces (a type of central heating system particularly popular in North America). This lead has continued into 2025 as more people realize that the pumps can lower fossil fuel emissions and energy bills.

This switch is not just happening in the US; countries worldwide are beginning – or continuing – to invest in these pumps. Sales in European countries have soared in the 21st-century, an accomplishment partly attributed to friendly government policy. The country with the most pumps relative to its population, Norway, has 632 heat pumps installed for every 1,000 households (the majority of these pumps service entire houses, unlike the Midea and Gradient systems discussed above). Despite this high ownership rate, 48 pumps were purchased in Norway for every 1,000 households in 2024.
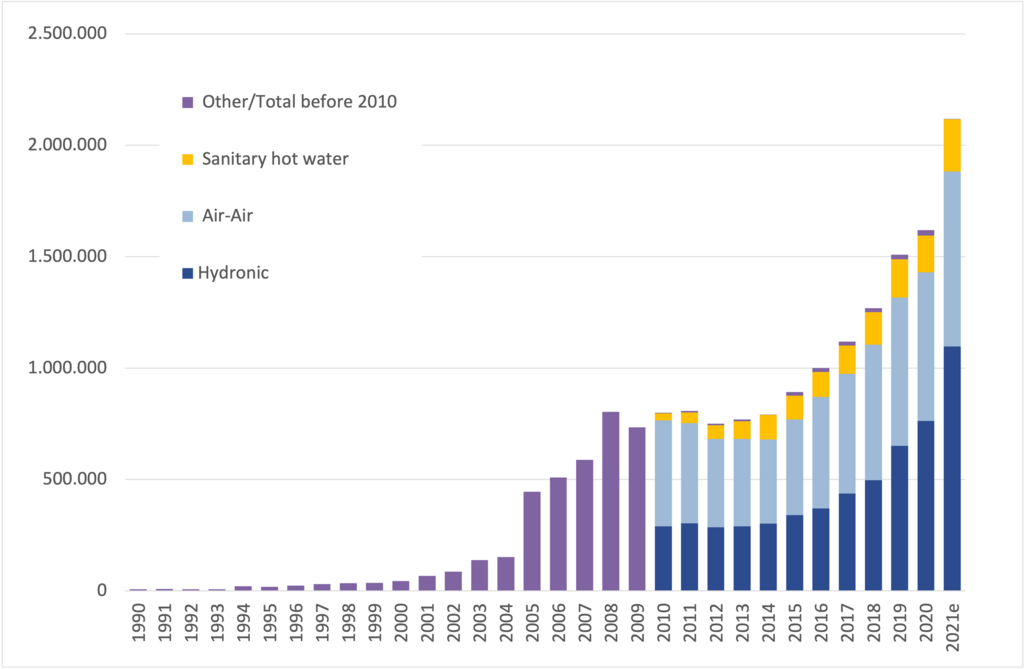
In spite of these promising statistics, heat pump sales in most economies have either slowed or slumped in recent years – particularly in Europe. Analysts suspect this is due to high interest rates, rising electricity prices, low consumer confidence, and low gas prices. While this is discouraging, pump sales and ownership rates remain higher than they were several years ago.
In 2023, New York Governor Kathy Hochul pledged to help the U.S. Climate Alliance (USCA) install 20,000,000 pumps across the U.S. The USCA is a coalition of 24 governors representing 54% of the United States population and 57% of its economy. The bipartisan group has successfully delivered on their promises of emissions reduction, climate resilience, economic growth, energy savings, and zero-carbon electricity standards that heat pumps are engineered to meet.
This coalition has proved that environmental action is popular, necessary, and possible. At a time when climate policy is under question, sustainable and feasible technologies – like heat pumps – need the investment of citizens, industries, and governments alike; no matter how small the scale.
So, how can you help? Since 2022, the US government has given a federal tax credit to citizens who install efficient heat pumps. The Energy Efficient Home Improvement Credit provides eligible homeowners up to $2,000 annually. Combined with other energy-efficient credits, US citizens can regain up to $3,200 every year. These monetary incentives offer another reason to consider switching to heat pumps, and similar policies are being enacted worldwide.
I am proud to live in a city that rewards and encourages the sustainability of citizens, corporations, and public works. As the severity and irreversibility of global warming loom, heat pumps offer us a breezy solution to polluting climate control systems. Eventually, NYC’s infamous boiler rooms and clanging pipes may become relics of the past.


Leave a comment