By Aashritha Shankar
~ 8 minutes
While the concepts of space and time were fundamental to the Newtonian world, centuries of digging deeper into the mechanics of our universe have uncovered that it isn’t all as simple as it seems. From Einstein’s Special Relativity to theories of multi-dimensional time, the science behind space and time has evolved into a complex field.
What are Extra Spatial Dimensions?
As scientists explored further into spacetime, theories of more dimensions of space, beyond the three we know, were suggested as a way to explain many of the phenomena that we cannot explain with only three dimensions. These ideas gained most of their traction from the pursuit to combine quantum mechanics with General Relativity, especially issues such as quantum gravity. These theories also attempt to address the rapid growth of the universe after the Big Bang.
What were the motivations to search for Extra Dimensions?
The idea of more dimensions began as a way to unify the fundamental forces of our universe. Modern theories regarding these ideas come from a drive to resolve some of the unaddressed issues of the Standard Model of physics. While the Standard Model is able to describe fundamental particles and the strong, weak, and electromagnetic forces, it is unable to describe gravity. In addition, the Standard Model cannot address dark matter and dark energy, which make up the majority of our universe.
One of the most significant problems in physics is the Hierarchy problem. It refers to the massive gap in strength between gravity and the other three fundamental forces. This extreme difference comes from the small scale of the strength of gravity in comparison to the other forces. Extra-Dimensions have attempted to resolve this by suggesting that while gravity may be just as strong as the other forces, its strength is leaked into the other dimensions, thus weakening it.
This search to discover extra dimensions is not only about solving these specific technical issues; it’s about the centuries-long quest to find a Theory of Everything. Physicists constantly strive to find simpler solutions to describe our universe rather than leaning on hyperspecific coefficients/constants.
While there are many theories involving extra-spatial dimensions, part 2 will focus on a few of the biggest and most influential theories so far.
Kaluza-Klein Theory
In 1919, Theodor Kaluza proposed his theory of four-dimensional space as an attempt to combine gravity and electromagnetism. This theory was later built upon by Oscar Klein in 1926.
In Kaluza’s attempt to combine these fundamental forces, he suggested a fourth, unseen spatial dimension. To create this system, he used Einstein’s equations and extended them into a fifth dimension. He found that the five-dimensional version of Einstein’s equations naturally created the four-dimensional version in one part. The equation had fifteen components, ten of which described our four-dimensional General Relativity. Four of the remaining five described the electromagnetic force through Maxwell’s equations, while the last dimension was the scalar field, which had no known use.
A key concept of Kaluza-Klein theory is that, rather than seeing electric charge as simply an event or calculation, it is represented as the motion of the fifth dimension. The attempt to create the simplest mathematical structure that could represent the five dimensions led to the assumption that no part of the five-dimensional Einstein equations relied explicitly on this fifth dimension. Instead, its presence was there to alleviate other issues in the Standard Model without disrupting the basic functions of Einstein’s equations. In order to do this, Kaluza created the cylinder condition, where he described all coordinate values in the fifth dimension to be zero, effectively hiding it at a macroscopic level, preserving the four dimensions that we experience.
Oscar Klein produced a physical explanation for the cylinder condition in 1926. He suggested that the fifth dimension was compactified and curled up into an unobservable circle with an incredibly small radius, explaining that this is why we are unable to witness the fifth dimension.
An interesting way to understand this is to think of a hose. From a distance, the hose looks like a single-dimensional line. However, the hose actually has two dimensions, both a dimension of length as well as a circular dimension.
This theory revolutionized how physicists thought about spacetime. In a letter to Kaluza that same year, Einstein wrote,
“The idea of achieving unification by means of a five-dimensional cylinder world never dawned on me […]. At first glance, I like your idea enormously. The formal unity of your theory is startling.” (Einstein, 1919)
Over time, Kaluza-Klein theory has been disproven due to its several fundamental flaws. Scientists have tested for Kaluza-Klein resonances, particles that would have to exist if the theory were to be true, and have found none. In addition, Kaluza-Klein theory only addresses gravity and electromagnetism but excludes the strong and weak forces. When incorporated with quantum mechanics, Kaluza-Klein theory predicts many incorrect values for otherwise known constants, showing massive discrepancies. Despite these issues, Kaluza-Klein theory has long been considered the first step into the exploration of extra-dimensions, becoming the precursor to many theories in the decades after. Its core idea- that hidden dimensions cause forces in our four dimensions-has been crucial to further exploration into the concept of spacetime.
String Theory and M-Theory
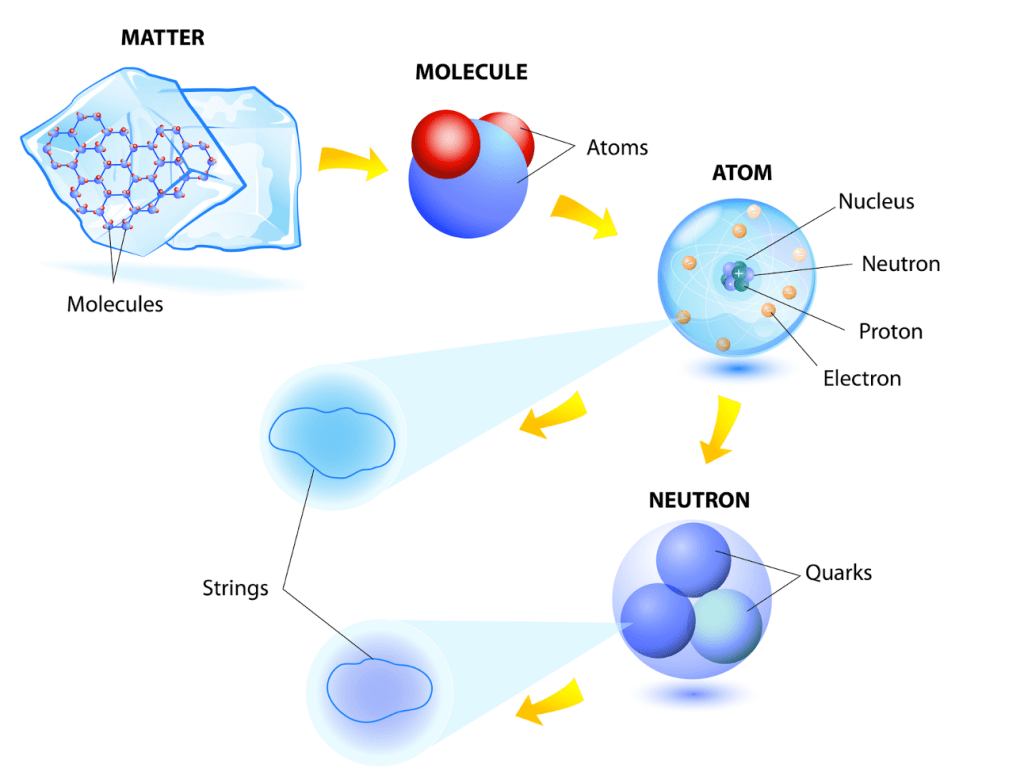
String Theory is a very common term, but few people actually know what it means. String theory proposed that instead of the universe being made up of zero-dimensional points, it is made up of strings that vibrate. The specific vibration of these strings would determine what they would be (photon, quark, etc.). The theory aimed to unify all of these different particles and properties into one thing: the string.
When physicists first began to work on String Theory, they found many mathematical issues, such as negative probabilities. In four dimensions, these strings don’t have enough space to produce the wide range of vibrations needed to create all the particles in the standard model. Thus, Superstring Theory suggests that these strings are ten-dimensional objects (nine dimensions of space and one of time). A major reason why physicists were happy with string theory at the time was that it naturally predicted a particle called a ‘graviton’. This particle would have the same effect as the force of gravity. Theoretical physicist Edward Witten has commented on this by saying,
“Not only does [string theory] make it possible for gravity and quantum mechanics to work together, but it […] forces them upon you.” (Edward Witten, NOVA, PBS)
M-Theory is an extension of String Theory that adds one more spatial dimension. Prior to its creation, different groups of physicists had created five versions of String Theory.
However, a true “Theory of Everything” should be one theory, not five possibilities.
M-Theory was created as an attempt to unify these five types of string theory. The key to the development of M-Theory was the discovery of mathematical transformations that took you from one version of String Theory to another, showing that these were not truly separate theories. M-theory theorized that these different versions were just different approximations of the same theory that could be unified by adding another dimension. M-Theory’s eleven-dimensional framework allowed for the unification of these five theories alongside the theory of supergravity.
M-Theory, similarly to Kaluza-Klein Theory, also proposes that the extra dimensions are curled up and compacted. M-Theory uses a specific geometric shape, known as a Calabi-Yau manifold, to create the physical effects we observe in our four dimensions from the other hidden seven. Calabi-Yau manifolds are a highly compact and complex type of manifold that are the foundation of M-Theory because they allow complex folding without affecting the overall curvature of our universe through a property called “Ricci-flatness”. The Calabi-Yau manifolds also have “holes” within their shapes that are thought to connect to the number of families of particles we experience in the Standard Model. This introduces the key concept that, instead of the fundamental laws of physics just being rules, they are actually geometric properties of our universe.
The biggest challenge that M-Theory is facing is its lack of experimental evidence. Predictions made by this model are not testable by currently available or foreseeable technology due to the high-dimensional microscopic levels required. Without making testable predictions, the theory remains just a theory for the time being.
Despite this lack of proof, many physicists still see M-Theory as a prominent candidate in our search for a “Theory of Everything”. Its mathematical consistency and its ability to unify both gravitational and quantum effects lead to it being considered highly promising.
However, while the math behind M-Theory is highly developed, it is not yet complete. The theory is still a work in progress as research is being conducted to better understand its structure and significance.
Meanwhile, critics believe that M-Theory is fundamentally flawed. Many of them believe that the “Landscape” problem is a significant reason that M-Theory is untrue. The “Landscape” problem is described as the fact that the theory predicts many different universes, each with its own set of physical laws. Critics believe that this prediction proves the unreliability of M-Theory and that a true “Theory of Everything” would be applicable only to our universe.
Overall, M-Theory has neither been proven nor disproven and remains a crucial area for future exploration.


Leave a comment